The coolest thing about electromagnetic relay is their construction. It's design is state of art because it include Mechanical, Electrical and Electronics engineering in designing. Electromagnetic relays are those relays which operate on faraday's electromagnetic induction principal. Further it is classified as below.
 |
| Fig-1 Classification of electromagnetic relays |
Electromagnetic attracted armature type relay:-
The most common form of electromagnetic relay consist of energizing coil wound around permeable iron core. This iron core has yoke as a fixed part and Spring loaded armature as a movable part. The armature is hinged or pivoted which allow it to move free when magnetic field attract it and close it's contacts.
Here coil has some parameter like Resistance, Rated voltage which is mention in it's manual. Rated voltage is mention on name plate of relay.
Coil's standard rated voltage is 24V, 48V, 110V, 250V DC. Resistance is depend upon rated voltage. DC coil is design based upon application.
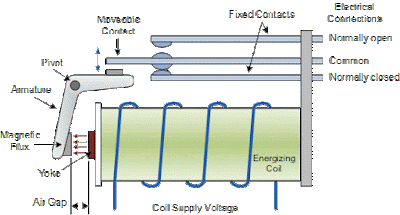 |
| Fig-2, Attracted Armature type unit |
 |
| Fig-3, Attracted armature type unit as per manual |
As you can see in diagram. When supply given to coil it form electromagnetic flux which pull armature piece which is fixed with pivot, when it pull toward coil ,upper armature which is placed on top of coil lifts up which result changeover of contacts.
It is designed such that it's electromagnetic field can capable to lift up contacts. If it cannot lift up contact then coil of relay become weak.
DC Supply given to relay let's analyze it from equation.
 |
| Fig-4, Force equation when DC Supply given |
As you can see from equation force of coil is directly propotional to square of current. If your applied voltage is capable to lift up contacts then your relay operate.
Here you can see force is unidirectional as it has only current component.
AC Supply given to relay let's analyze it from equation.
 |
| Fig-5, Force equation when AC Supply given |
As you can see in above image, force equation has two component. First one is unidirectional component which is similiar to dc equation. Another one has cos2wt component which suggest it has twice of supply frequency.
Pulsating component of force result into attraction and repulsion which result into chattering of contact and damage in long time.
AC Voltage operated relay also available in market but in their construction, they used rectifier to convert AC into DC then it give to DC coil for smooth operation.
AC Voltage operated relay also available in market but in their construction, they used rectifier to convert AC into DC then it give to DC coil for smooth operation.
Let as take image of electromagnetic relay and analyze some thing.
 |
| Fig-6, Attracted armature type Relay |
Make:- GEC ALSTHOM
Type:- VAA (Voltage operated attracted armature type)
Model No:- VAA 11
Operating Voltage:- 110V / 250V DC.
Now you have question why two rated voltage for single coil?
Coil of this relay has 110V DC rated voltage but if your panel's control supply is 250V than don't worry this relay can be used in that panel too.
HOW?
In the construction of this relay one resistance is connected in series with coil internally so if you want to use this relay for 110V then short this resistance so your applied voltage is directly gone to coil.
If you want to use for 250V DC then connect your supply lead directly with coil as resistance is in series with coil so voltage drop occurs across resistance and your coil get 110V only.
Operating Voltage range:- This relay operate satisfactorly between 75% to 125% of rated voltage.
Operating time:- 15-20 msec at Rated Voltage.
Contact of Electromagnetic type relays
Electromagnetic relay have this type of contact which is shown in above figure. Contact made of steel but contact tip which actually contact is made of special material as below.
1. Single Pole Single throw (SPST)
2. Single Pole Double throw (SPDT)
3. Double Pole Single throw (DPST)
4. Double Pole Double throw (DPDT)
For Testing of electromagnetic relay refer my other posts.
Type:- VAA (Voltage operated attracted armature type)
Model No:- VAA 11
Operating Voltage:- 110V / 250V DC.
Now you have question why two rated voltage for single coil?
Coil of this relay has 110V DC rated voltage but if your panel's control supply is 250V than don't worry this relay can be used in that panel too.
HOW?
In the construction of this relay one resistance is connected in series with coil internally so if you want to use this relay for 110V then short this resistance so your applied voltage is directly gone to coil.
If you want to use for 250V DC then connect your supply lead directly with coil as resistance is in series with coil so voltage drop occurs across resistance and your coil get 110V only.
Operating Voltage range:- This relay operate satisfactorly between 75% to 125% of rated voltage.
Operating time:- 15-20 msec at Rated Voltage.
Contact of Electromagnetic type relays
 |
| Fig-7, Contact Profile |
1. Ag (Fine Silver)
Electrical and thermal conductivity highest of all the metals
low CRM is inexpensive and widely used
2. AgCu (Silver Copper)
Hard silver contact, better wear resistance, less tendency to arc and weld but higher CRM.
3. AgCdO (Silver Cadmium Oxide)
good wear resistance and arc extingushing properties.
4. AgW (Silver Tungsten)
Hardness and melting point is high, arc resistance is excellent.
High contact pressure is required to reduce CRM.
When Contact is NO, resistance is infinite but when it close, ideally contact resistance is zero but practically it is some value depend on operation of relay.
In Contactor application, To open the contactor, NC contact of relay is connected in series with contactor clsoing coil. So When NC contact open it break current and when open, some spark appear across contact if this type of operation done so much time then carbon jammed on contact tips leads to increase in contact resistance.Next time when you start contactor then it may be happen that your contactor cannot close as voltage drop occurs at contact resistance. For smooth operation you need to remove carbon from contacts.
Contact Types:-.
1. Single Pole Single throw (SPST)
2. Single Pole Double throw (SPDT)
3. Double Pole Single throw (DPST)
4. Double Pole Double throw (DPDT)
 |
| Fig-8, Types of Contacts |
Post a Comment