NETWORK CONFIGURATION
Electrical power distribution network can also be distinguished according to their type of meshing. The following basic configuration are distinguished.
- Radial Network
- Ringed Network
The radial network is the most simple form. It's advantage is easy monitoring & Protection, Fast fault localisation and simple operational management. If requirement of reliablility is high, each supply line can be fed from independent supply network. Due to fact that network are independent of from each other, a fault in one network will not affect the other one.
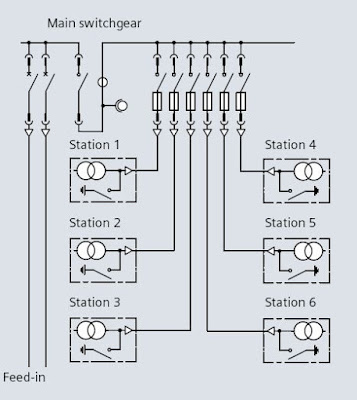 |
| RADIAL NETWORK |
As shown in image, all transformer are connected in parallel. For protection of individual feeder Overcurrent and earthfault protection is employed.
Ringed Network
In combination with a ring line as an extension of the radial network, a ringed network can be built up. In this system, each transformer is feed with two feeder but in different path. It create ring which start from substation busbar, then it goes in load center, then return to substation bubar. The following image will clear your vision toward ringed network.
 |
| RINGED NETWORK |
As shown in image, In case of cable fault in an open type ringed network, all station downward of the fault location upto the normally open switch will fail. In case of low voltage side meshing of the ring station, the failure of large sub-ring could result in overload and disconnection of non affected transformers, whereas cable fault in radial network merely results in the failure of one station. It require shorter cable length but the cable cross section must be higher owing to the transmission of higher capacities from one end ringpoint to other.
COMMON DEFINITION
- Voltage
- Current
- Frequency
- Short Circuit Power
- Operating Voltage:- It is applied across the equipment terminals. It is the service or network voltage where the equipment is fitted. It is subjected to fluctuation linked to the network operation, load level, etc...
- Rated voltage :- This is the maximum rms value of the voltage that the equipment can withstand under normal operating condition.
- Rated Insulation level :- For MV Switchgear, two withstand voltages are specified
- Power frequency withstand voltage:- It is defined as how much your switchgear can withstand your normal frequency voltage.
- Lightning impulse withstand voltage:- It is voltage of external origin like lightning fall on line. For this test waveshape of 1.2/50 microsecond will be applied. This performance known as Basic Insulation level (BIL).
Current
- Rated Normal current :- This is the r.m.s. current value that equipment can withstand when it is close, without exceeding temperature rise allowed in standards.
- Rated Short time withstand current :- The r.m.s. value of current that equipment can withstand for short time when it is close. It is defined in kA for 1,2 or 3 seconds and is used to define the thermal withstand of the equipment.
- Rated peak withstand current:- It is peak value of short time current that equipment can withstand when it is close, It is defined as electrodynamic withstand of equipment.
- Operating current:- The r.m.s. Value of current which actually flow through equipment. to calculate it power must be known.
Frequency
- 50Hz in Europe, Africa, Asia, Oceania, South of South america.
- 60Hz in North america, North of south america, Kingdom of Saudi arabia, Philippines, Taiwan, South Korea, South of Japan.
Short Circuit Power:- It is depends directly on the network configuration and impedance of its components: lines, cables, transformers, motors. It is the maximum power that can provide to an installation during fault. It is expressed in MVA or in kA for given operating voltage. Possible source of short circuit powers are, Network incomers from power transformer, Generator incomer, Power back feed due to rotary sets(motors) or via MV/LV Transformers.
- Short Circuit Current:- When any fault occur in the system then huge amount of current will flow it's called short circuit current. It's value allow us to choose relay, fuse, Current transformers.
Post a Comment